Product Description
Applications
A semi-trailer suspension is an important part connecting the traveling device and the frame of the semi-trailer.
All forces are all transmitted through the suspension system. And the suspension reduces the impact of harsh roads on the vehicle, plays a shock absorption effect, and improves the ride comfort of the vehicle.
Semi-trailer suspensions are widely applied to skeletal trailers, lowbed trailers, flatbed trailers, dump trailers, car transport trailers, oil tank trailers, van trailers, full trailers, wood transport trailers, agricultrucal vehicles, etc. Classification of suspension indlude German series suspensions, American series suspensions, bogie/boogie suspension series, air suspension series, rigid suspension series, CZPT suspensions, ROR suspensions, HENRED suspensions, semi-trailer suspensions, trailer suspensions and agricultural series, etc.
Features
| QC management system | Implementing IATF 16949-2016 | ||||||
| Services quality management system | Implementing ISO 9001-2015 | ||||||
| Warranty | 18 months since shipping date | ||||||
| Quality testing passed | An independent lab in China | ||||||
| Raw material for suspensions | Q235 from China’s TOP-3 steel mills can achieve a longer life under higher loads | ||||||
| Steel plate cutting by | CNC Plasma Cutting Machines | ||||||
| Press forming by | 40-800 ton hydraulic press machines with hundreds of precision molds | ||||||
| Hanger welding by | Automatic CNC welding robots/lines with hundreds of precise fixture toolings | ||||||
| Smooth surface by | Shot-peening | ||||||
| Painting by | Automatic coating line | ||||||
| Producing leaf springs and casting parts by | Ourselves to ensure the lead time and quality are under control | ||||||
| Equalizer bushes | Using taper or greaseless powdered metal ones to be more durable | ||||||
| Arm bushes | Using natural rubber ones to be more durable | ||||||
| Adjustable arms screw by | Galvanized anti-rust treatment | ||||||
| Sets of annual output | 50,000 | 1180 | 441 | 433 | 183 | 13,000 * 2 | FW885711A |
| WDA2223908801 | 1220 | 481 | 473 | 223 | 13,000 * 2 | FW885712A | |
| WDA2253908801 | 1250 | 511 | 503 | 253 | 13,000 * 2 | FW885713A | |
| WDA2164908801 | 1180 | 422 | 414 | 164 | 13,000 * 2 | FW885711B | |
| WDA2204908801 | 1220 | 462 | 454 | 204 | 13,000 * 2 | FW885712B | |
| WDA2234908801 | 1250 | 492 | 484 | 234 | 13,000 * 2 | FW885713B |
WD88.03 Tri (3-axle) Suspensions
| Model | Height of towing plate (mm) | A1 (mm) | A2 (mm) | A3 (mm) | H (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA3185908801 | 1180 | 457 | 448 | 435 | 185 | 13,000 * 3 | FW880301A |
| WDA3225908801 | 1220 | 497 | 488 | 475 | 225 | 13,000 * 3 | FW880302A |
| WDA3255908801 | 1250 | 527 | 518 | 505 | 255 | 13,000 * 3 | FW880303A |
| WDA3166908801 | 1180 | 438 | 429 | 416 | 166 | 13,000 * 3 | FW880301B |
| WDA3206908801 | 1220 | 478 | 469 | 456 | 206 | 13,000 * 3 | FW880302B |
| WDA3236908801 | 1250 | 508 | 499 | 486 | 236 | 13,000 * 3 | FW880303B |
Note:
(1) Demension “A1, A2, A3”: unladen
(2) Suitable for round/square axles
(3) Suggested leaf spring: 90×16×7 pcs
-WD86 Type Heavy Duty Suspension Series
WD86.02 Tandem (2-axle) Suspensions
| Model | Height of towing plate (mm) | A1 (mm) | A2 (mm) | H (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA2183908601 | 1180 | 473 | 465 | 183 | 16,000 * 2 | FW865711A |
| WDA2223908601 | 1220 | 513 | 505 | 223 | 16,000 * 2 | FW865712A |
| WDA2253908601 | 1250 | 543 | 535 | 253 | 16,000 * 2 | FW865713A |
| WDA2164908601 | 1180 | 454 | 446 | 164 | 16,000 * 2 | FW865711B |
| WDA2204908601 | 1220 | 494 | 484 | 204 | 16,000 * 2 | FW865712B |
| WDA2234908601 | 1250 | 526 | 518 | 234 | 16,000 * 2 | FW865713B |
WD86.03 Tri (3-axle) Suspensions
| Model | Height of towing plate (mm) | A1 (mm) | A2 (mm) |
A3 (mm) | H (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA3183908601 | 1180 | 489 | 480 | 467 | 183 | 16,000 * 2 | FW860301A |
| WDA3223908601 | 1220 | 529 | 520 | 507 | 223 | 16,000 * 2 | FW860302A |
| WDA3253908601 | 1250 | 599 | 550 | 537 | 253 | 16,000 * 2 | FW860303A |
| WDA3164908601 | 1180 | 470 | 461 | 448 | 164 | 16,000 * 2 | FW860301B |
| WDA3204908601 | 1220 | 510 | 501 | 588 | 204 | 16,000 * 2 | FW860302B |
| WDA3234908601 | 1250 | 540 | 531 | 518 | 234 | 16,000 * 2 | FW860303B |
Note:
(1) Demension “A1, A2, A3”: unladen
(2) Suitable for round/square axles
(3) Suggested leaf spring: 90×16×9 pcs
-WD86 Type Heavy Duty Underslung Suspension Series
WD86.21 Tandem (2-axle) Underslung Suspensions
| Model | L1 (mm) | L2 (mm) | L3 (mm) | L4 (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA | 495 | 1310 | 1135 | 1165 | 16,000 * 2 | FW86.2/1310/250/BQ6/9 |
| WDA | 495 | 1360 | 1160 | 1190 | 16,000 * 2 | FW86.2/1360/250/BQ6/9 |
WD86.31 Tandem (2-axle) Underslung Suspensions
| Model | L1 (mm) | L2 (mm) | L3 (mm) | L4 (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA | 495 | 1310 | 1135 | 1165 | 16,000 * 2 | FW86.3/1310/250/BQ6/9 |
| WDA | 495 | 1360 | 1160 | 1190 | 16,000 * 2 | FW86.3/1360/250/BQ6/9 |
Note:
(1) Suitable for round/square axles
(2) Suggested leaf spring: 90×16×9 pcs
-WD68 Type Stamping Suspension Series
WD68.21 AR5 Tandem (2-axle) Suspensions
| Model | A1 (mm) | A2 (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA244571801 | 440 | 440 | 11,000 * 2 | FW68.21HHAR05 |
| WDA2415756801 | 415 | 415 | 11,000 * 2 | FW68.21MMAR05 |
| WDA239571801 | 390 | 390 | 11,000 * 2 | FW68.21LLAR05 |
| WDA244571802 | 440 | 415 | 11,000 * 2 | FW68.21HMAR05 |
| WDA2415756802 | 415 | 390 | 11,000 * 2 | FW68.21MLAR05 |
WD68.31 AR5 Tri (3-axle) Suspensions
| Model | A1 (mm) | A2 (mm) | A3 (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA344571801 | 440 | 440 | 440 | 16,000 * 2 | FW68.31HHHAR05 |
| WDA3415756801 | 415 | 415 | 415 | 16,000 * 2 | FW68.31MMMAR05 |
| WDA339571801 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 16,000 * 2 | FW68.31LLLAR05 |
| WDA344571802 | 440 | 415 | 390 | 16,000 * 2 | FW68.21HMLAR05 |
Note:
(1) Demension “A1, A2, A3”: unladen
(2) Suitable for round/square axles
(3) Suggested leaf spring: 75×13×8 pcs
-WD66 Type Lightweight Suspension Series
WD66.22 AR5 Tandem (2-axle) Underslung Suspensions
| Model | A1 (mm) | L1 (mm) | L2 (mm) | L3 (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA239571601 | 390 | 482.5 | 1245 | 1105 | 10,000 * 2 | FW66.2/1245/390/AR5/3L |
| WDA2415756601 | 415 | 482.5 | 1245 | 1105 | 10,000 * 2 | FW66.2/1245/390/AR5/3L |
| WDA244571601 | 440 | 482.5 | 1245 | 1105 | 10,000 * 2 | FW66.2/1245/390/AR5/3L |
Note:
(1) Demension “A1, A2, A3”: unladen
(2) Suitable for round/square axles
(3) Suggested leaf spring: 75×22×3 pcs
-WD20 Type Heavy Duty Suspension Series
WD20.02 Tandem (2-axle) Suspensions
| Model | Height of towing plate (mm) | A1 (mm) | A2 (mm) | H (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA2183157101 | 1180 | 489 | 481 | 183 | 20,000 * 2 | FW25711A |
| WDA2223157101 | 1220 | 529 | 521 | 223 | 20,000 * 2 | FW25712A |
| WDA2253157101 | 1250 | 559 | 551 | 253 | 20,000 * 2 | FW25713A |
| WDA2164157101 | 1180 | 470 | 462 | 164 | 20,000 * 2 | FW25711B |
| WDA | 1220 | 510 | 502 | 204 | 20,000 * 2 | FW25712B |
| WDA2234157101 | 1250 | 540 | 532 | 234 | 20,000 * 2 | FW25713B |
WD20.03 Tri (3-axle) Suspensions
| Model | Height of towing plate (mm) | A1 (mm) | A2 (mm) | A3 (mm) | H (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA3183157101 | 1180 | 505 | 496 | 483 | 183 | 20,000 * 2 | FW200301A |
| WDA3223157101 | 1220 | 545 | 536 | 523 | 223 | 20,000 * 2 | FW200302A |
| WDA3253157101 | 1250 | 575 | 566 | 553 | 253 | 20,000 * 2 | FW200303A |
| WDA3164157101 | 1180 | 486 | 477 | 464 | 164 | 20,000 * 2 | FW200301B |
| WDA | 1220 | 526 | 517 | 504 | 204 | 20,000 * 2 | FW200302B |
| WDA3234157101 | 1250 | 556 | 547 | 534 | 234 | 20,000 * 2 | FW200303B |
Note:
(1) Demension “A1, A2, A3”: unladen
(2) Suitable for round/square axles
(3) Suggested leaf spring: 100×16×10 pcs
German type Suspension Series (BPW type)
WDGB02 Tandem (2-axle) Suspensions
| Model | H (mm) | A (mm) | C (mm) | D (mm) | E (mm) | Leaf spring |
| WDGB21551001201 | 155 | 490 | 1295 | 615 | 2610 | 100×12×12 |
| WDGB21551001401 | 155 | 514 | 1295 | 615 | 2610 | 100×12×14 |
WDGB03 Tri (3-axle) Suspensions
| Model | H (mm) | A (mm) | C (mm) | D (mm) | E (mm) | Leaf spring |
| WDGB31551001201 | 155 | 490 | 1295 | 615 | 3970 | 100×12×12 |
| WDGB31551001401 | 155 | 514 | 1295 | 615 | 3970 | 100×12×14 |
Note:
(1) Demension “A”: unladen
(2) Suitable for round/square axles
(3) Suggested leaf spring: 100×12×12 pcs, 100×14×12 pcs, 100×12×14 pcs
German type Suspension Series (SAF type)
WDGS02 Tandem (2-axle) Suspensions
| Model | H (mm) | A (mm) | C (mm) | D (mm) | E (mm) | Leaf spring |
| WDGS21551001201 | 155 | 500 | 1295 | 615 | 2610 | 100×12×12 |
| WDGS21551001401 | 155 | 524 | 1295 | 615 | 2610 | 100×12×14 |
WDGS03 Tri (3-axle) Suspensions
| Model | H (mm) | A (mm) | C (mm) | D (mm) | E (mm) | Leaf spring |
| WDGS21551001201 | 155 | 500 | 1295 | 615 | 2610 | 100×12×12 |
| WDGS21551001401 | 155 | 524 | 1295 | 615 | 2610 | 100×12×14 |
Note:
(1) Demension “A”: unladen;Note:
(2) Suitable for round/square axles
(3) Suggested leaf spring: 100×12×12 pcs, 100×14×12 pcs, 100×12×14 pcs
Production
Workshops of CZPT Autoparts semi trailer suspensions:
(Raw material workshops, Components workshops, Mechanical suspension processing workshops, Semi trailer suspensionAssembly workshops, Painting line)
Processes & equipment of CZPT Autoparts semi trailer suspensions:
- Steel Plate Material→ 2. Steel Plate CNC Automatic Cutting→ 3. Hangers punching→ 4. Hangers Forming→ 5. Hangers Welding→ 6. Sleeve(A & B) Welding→ 7. Shot Peening→ 8. Painting→ 9. Laser marking→ 10. Assembling→ 11. Packing→ 12. Warehousing)
Products and logistics of CZPT Autoparts semi trailer suspensions:
(Mechanical suspension final production, Suspension hangers, Components of semi trailer suspensions, Suspension warehousing, Suspension packing, trailer suspension container loading)
Other types of CZPT Autoparts semi trailer suspensions:
(Germany BPW type mechanical suspension, Germany SAF type mechanical suspension, American CZPT type suspension with square beam, American CZPT underslung type suspension with square beam, American CZPT type suspension with round beam, American CZPT underslung type suspension with round beam)
Other types of CZPT Autoparts semi trailer suspensions:
(YTE casting type suspension, ROR casting type suspension, Henred Fruehauf type suspension, Agricultural trailer suspension)
Components
Components & spare parts of CZPT Autoparts semi trailer suspensions:
(Font hangers, Middle hangers, Rear hangers, Supension equalizers, Equalizer pins, Leaf springs, Fix torques, Adjustable torques, U-bolts, etc.)
Besides trailer mechanical suspensions, CZPT Autoparts also supply different types of semi trailer components as below:
| After-sales Service: | 18 Months |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 18 Months |
| Material: | Steel |
| Certification: | ISO/TS16949, ISO9001 |
| Car Make: | Benz, BMW, Toyota, Jeep, Nissan, Ford, Volvo, Mazda |
| Position: | Rear |
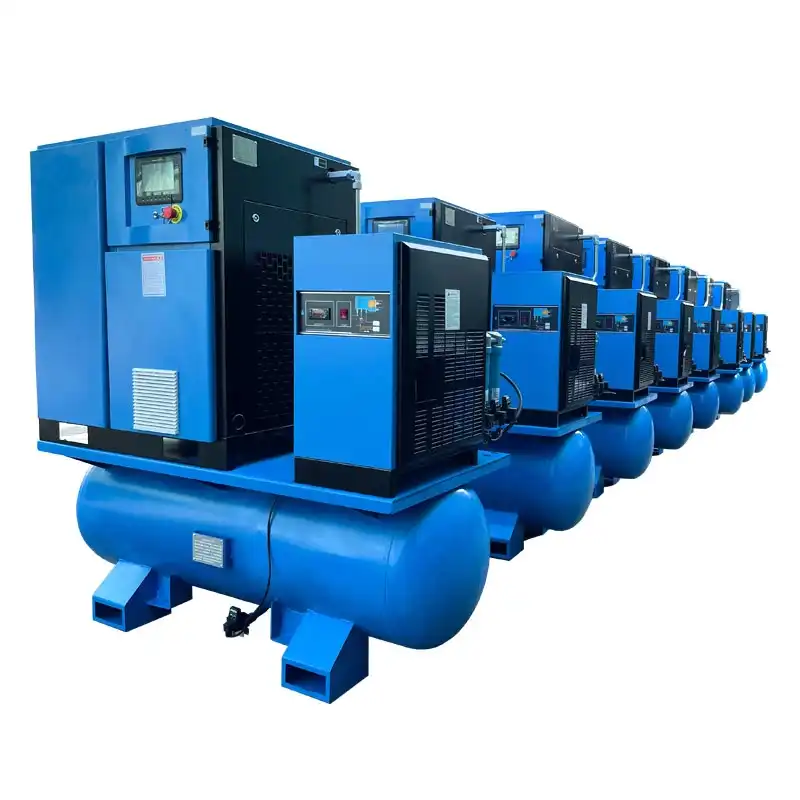

How to Choose the Right Air Compressor
An air compressor uses pressurized air to power a variety of tools. They are most commonly used to power nailers and impact wrenches. Other popular uses for air compressors include paint sprayers and impact wrenches. While all air compressors have the same basic construction, their specialty differs. Ultimately, their differences come down to the amount of air they can push. Read on for information on each type of air compressor. These tools are great for many different purposes, and choosing the right air compressor depends on your specific needs.
Electric motor
While purchasing an electric motor for air compressor, compatibility is a key factor. Not all motors work with the same type of air compressor, so it’s important to check the manufacturer’s instructions before purchasing. By doing this, you can avoid wasting money on an incompatible motor. Another important consideration is speed. A motor’s speed is its rate of rotation, measured in revolutions per minute. It is critical that you purchase a motor with sufficient speed to meet the needs of your air compressor.
Typically, an electric motor for air compressor is 1.5 hp. It is ideal for use with medical equipment and metal-cutting machines. It also performs well under continuous operation and offers a high efficiency and energy-saving performance. Moreover, it features an attractive price, making it a good choice for a wide range of applications. If you are looking for a motor for an air compressor, look no further than a ZYS series.
A motor’s protection class indicates how the motor will operate. Protection classes are specified by the IEC 60034-5. These are stated with two digits and represent the protection against solid objects and water. For example, an IP23 rating means that the motor will be protected from solid objects, while IP54 means that it will protect from dust and water sprayed from all directions. It is vital to choose a motor with the correct protection class for your air compressor.
When choosing an electric motor, you should consider whether it’s compatible with the brand of air compressor. Some may be compatible, while others may require advanced electronics skills to repair. However, most air compressors are covered by warranty, so it’s important to check with the manufacturer if the warranty is still in effect before you spend a dime on a replacement. The motor should be replaced if it has failed to perform as designed.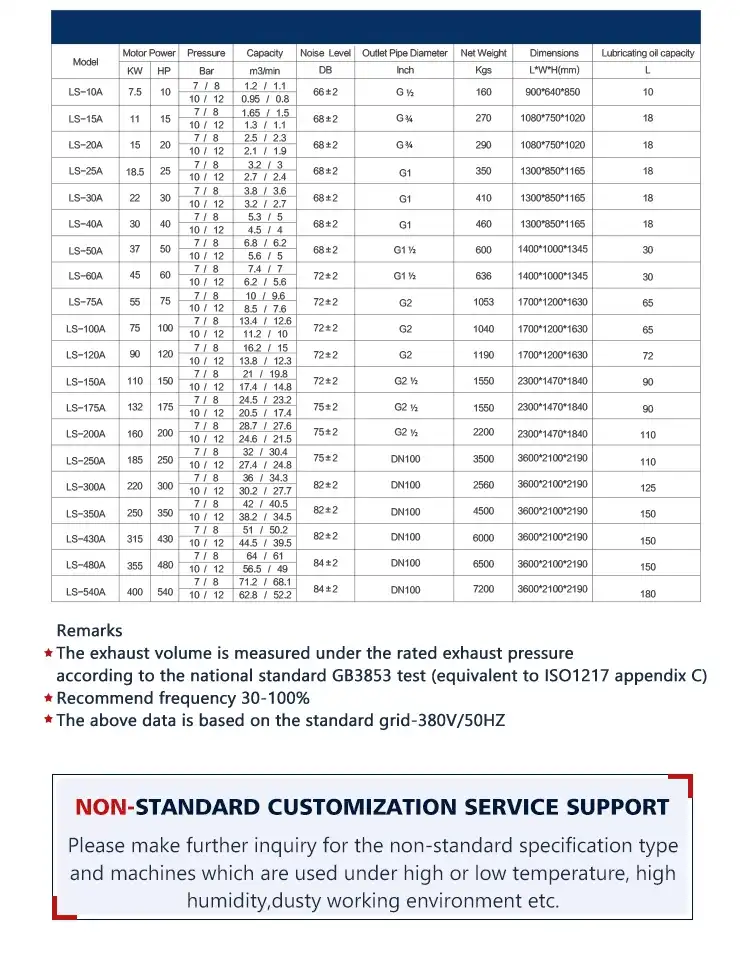
Oil bath
Air compressors require proper lubrication to function efficiently. The piston must draw air with minimal friction. Depending on their design, air compressors can either be oil-lubricated or oil-free. The former uses oil to reduce piston friction, while the latter splashes it on the cylinder bearings and walls. Such air compressors are commonly known as oil-flooded air compressors. In order to keep their oil baths clean, they are recommended for use in locations with high dust levels.
Start/stop control
An air compressor can be controlled by a start/stop control. This type of control sends a signal to the main motor that activates the compressor when the demand for air falls below a preset limit. This control strategy is effective for smaller air compressors and can be useful for reducing energy costs. Start/stop control is most effective in applications where air pressure does not change frequently and where the compressor is not required to run continuously.
To troubleshoot this problem, you need to check the power supply of your compressor. To check the supply side, use a voltage monitor to determine if power is flowing to the compressor. Ensure that the power supply to the compressor is steady and stable at all times. If it fluctuates, the compressor may not start or stop as expected. If you cannot find the problem with the air compressor power supply, it may be time to replace it.
In addition to the start/stop control, you may want to purchase additional air receivers for your air compressor. These can increase the capacity of air stored and reduce the number of times it starts and stops. Another way to decrease the number of starts per hour is to add more air receivers. Then, you can adjust the control to match your requirements. You can also install a pressure gauge that monitors the compressor’s performance.
Start/stop control for air compressors can be complex, but the basic components are relatively easy to understand. One way to test them is to turn the compressor on or off. It is usually located on the exterior of the motor. If you’re unsure of the location of these components, check the capacitors and make sure that the air compressor is not running while you’re not using it. If it does, try to remove the capacitor.
Variable displacement control is another way to adjust the amount of air flowing into the compressor. By controlling the amount of air, the control can delay the use of additional compressors until more required air is available. In addition to this, the device can also monitor the energy used in the compressor. This control method can result in substantial energy savings. You can even save on the amount of electricity by using variable displacement control. It is essential for efficient compressed air systems.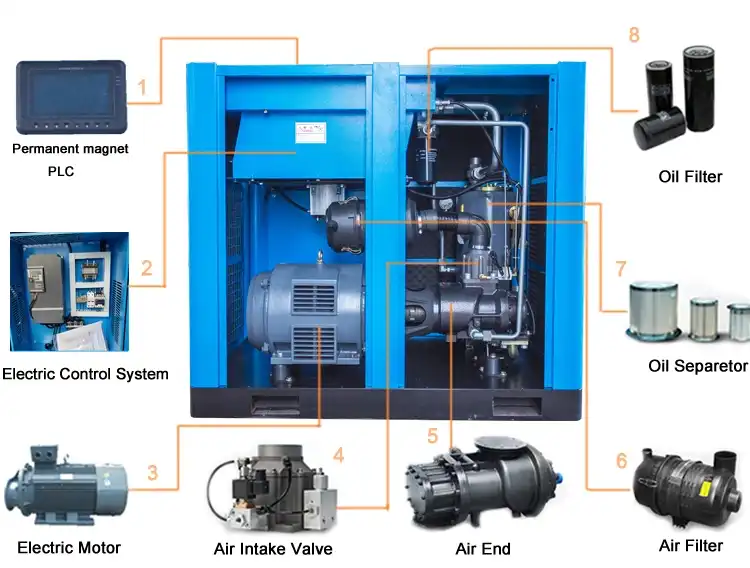
Variable speed drive
A VFD, or variable frequency drive, is a type of electric motor that adjusts its speed to match the demand for air. It is an efficient way to reduce energy costs and improve system reliability. In fact, studies have shown that a 20% reduction in motor speed can save up to 50% of energy. In addition, a VFD can monitor additional variables such as compressor oil pressure and motor temperature. By eliminating manual checks, a VFD will improve the performance of the application and reduce operating costs.
In addition to reducing energy costs, variable-speed drives also increase productivity. A variable-speed air compressor reduces the risk of system leaks by 30 percent. It also reduces the risk of system leaks by reducing pressure in the system. Because of these advantages, many governments are promoting this technology in their industries. Many even offer incentives to help companies upgrade to variable-speed drives. Therefore, the variable-speed drive can benefit many air compressor installations.
One major benefit of a variable-speed drive is its ability to optimize energy use. Variable frequency drives are able to ramp up and down to match the demand for air. The goal is to optimize the pressure and flow in the system so that the best “dead band” occurs between forty percent and eighty percent of full load. A variable-speed compressor will also increase energy efficiency because of its programmability.
A variable-speed air compressor can also be used to control the amount of air that is compressed by the system. This feature adjusts the frequency of power supplied to the motor based on the demand. If the demand for air is low, the frequency of the motor will reduce to save energy. On the other hand, if there is an excess demand for air, the variable-speed compressor will increase its speed. In addition, this type of air compressor is more efficient than its fixed-speed counterpart.
A VFD has many benefits for compressed air systems. First, it helps stabilize the pressure in the pipe network, thereby reducing the power losses due to upstream pressure. It also helps reduce the power consumption caused by fluctuations in upward pressure. Its benefits are also far-reaching. And as long as the air pressure and air supply is properly sized, a VFD will help optimize the efficiency of compressed air systems.


editor by CX 2023-05-24